Lipid Nanodiscs Assembly Technology
Lipid Nanodiscs are disc-like lipid bilayer structures with a diameter of 8-16 nm, stabilized by two encircling amphiphilic helical proteins, known as membrane scaffold proteins, or MSPs, to make them soluble in water. MSPs can be seen as scaled-down versions of Apolipoprotein A-I, which surrounds the lipid bilayer to form a membrane-like disc structure. The hydrophobic residues of MSPs are located internally and can interact with the hydrophobic tails of phospholipid molecules, while the hydrophilic residues are located laterally, which makes the lipid nanodiscs extremely soluble in water. By encasing membrane proteins in Lipid Nanodiscs, it is possible to mimic their natural state on the cell membrane while maintaining their spatial structure and activity, with the transmembrane domain enclosed in the lipid bilayer. The size of Lipid Nanodiscs depends on the length of the membrane scaffold protein and the molar ratio of lipids used in the self-assembly process. Therefore, the molar ratio of MSPs to phospholipids is crucial for optimizing yield. Uniform and monodispersed bilayer Lipid Nanodiscs can be obtained when the optimal molar ratio of MSP to phospholipid is achieved.
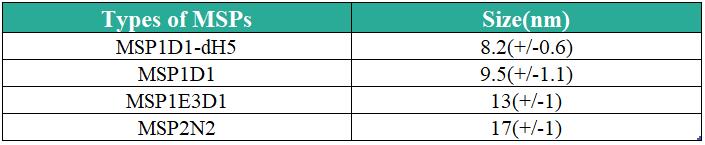
Table 1. Types and sizes of MSPs
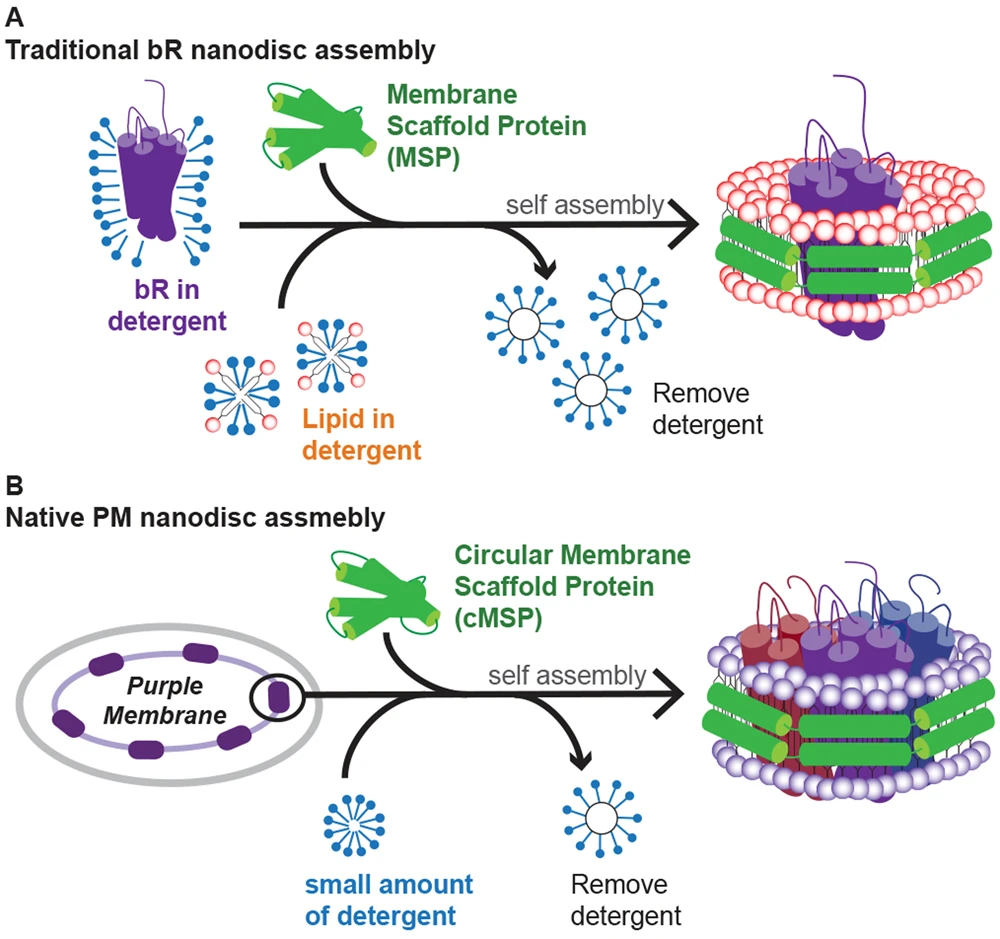
Yeh, V.; et al. Sci Rep. 2018.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the nanodisc assembly producing
Why Choose Lipid Nanodiscs Assembly Technology at CryoEM-Solutions
1.Ensure that the protein can fold normally and maintain a stable conformation
Lipid Nanodiscs effectively mimic the phospholipid bilayer structure of natural cellular membranes, providing an environment for membrane proteins that facilitates normal folding and ensures spatial conformational stability.
2.Suitable for Cryo-EM structural analysis
The optimal molar ratio of membrane scaffold proteins to phospholipids ensures the formation of bilayered homogeneous and monodisperse Lipid Nanodiscs, which is more suitable for Cryo-EM single particle analysis (SPA).
3.Capable of loading various types of membrane proteins
A variety of Lipid Nanodiscs can be adapted to accommodate different membrane proteins for loading requirements, including different sizes, different lipid types, and different tag types, etc.
The Applications of Lipid Nanodiscs
MPs (Membrane proteins, MPs) are indispensable elements in life processes, they play a vital role in the exchange of substances, information, and energy between cells and the external environment. MPs are also the primary targets of most therapeutic drugs in the industry. However, membrane proteins may experience insolubility or dysregulation of activity in an environment lacking a phospholipid bilayer. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a viable method to enable membrane proteins to be stabilized in the extracellular environment.
With its excellent performance, Lipid Nanodiscs successfully overcome the problem of the stable existence of membrane proteins in the extracellular environment after extraction. Lipid Nanodiscs Assemble technology provides a powerful tool for the isolation, purification, structural elucidation, and functional characterization of membrane proteins.








